Patient will have a ruddy face (facial plethora), high blood pressure, and itching that occurs after exposure to water e.g. after bath/ shower (aquagenic pruritis). Physical exam will show splenomegaly. Some patients may present with burning in hands/ feet (erythromelalgia), transient visual disturbances, bleeding, and gouty arthritis (increased RBC turnover). CBC will show very high hemoglobin and hematocrit, high platelet count and WBC count.
Increased blood viscosity is responsible for the visual disturbances, the hypertension, etc.
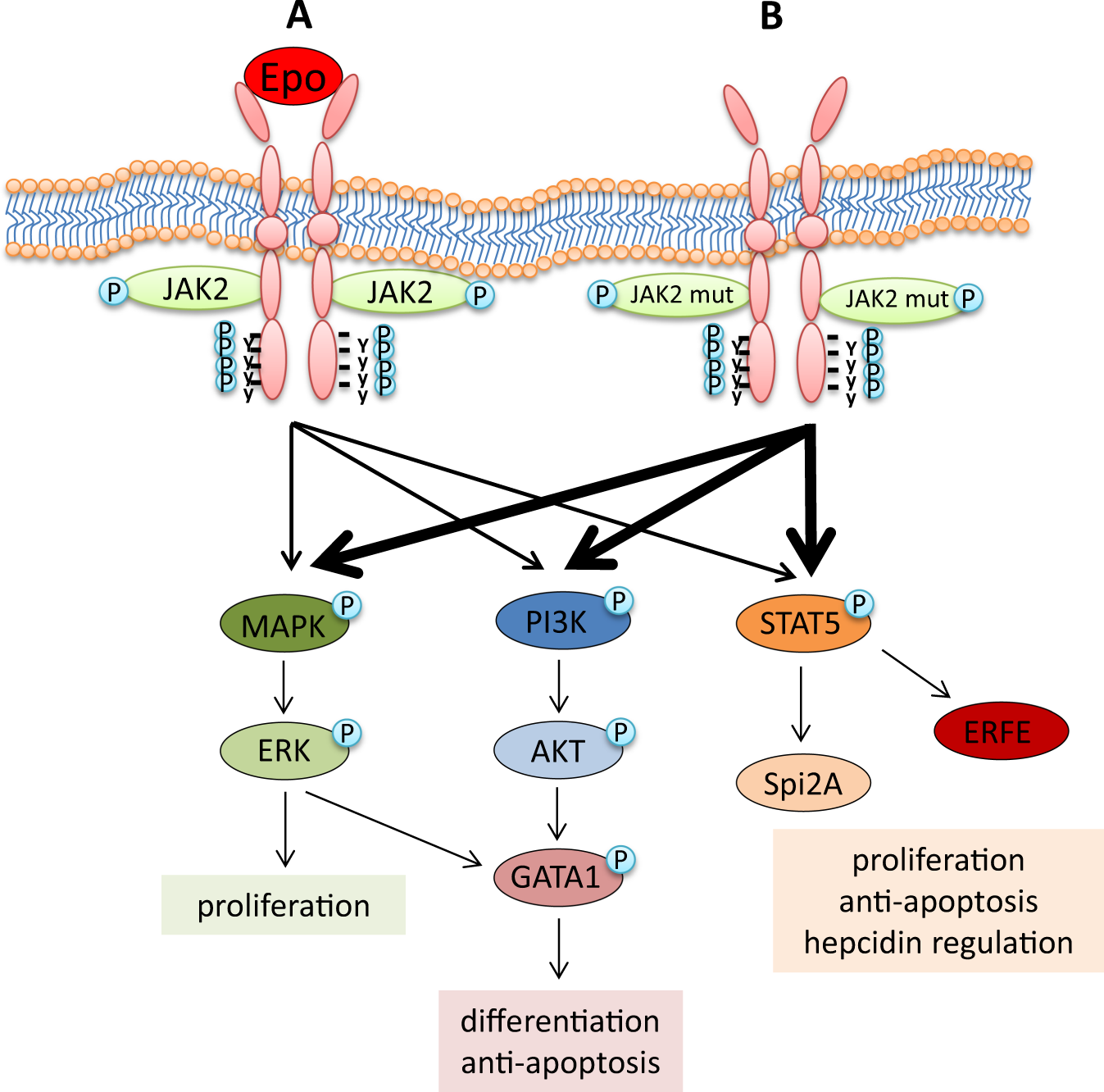
It is important to know the mutation responsible for PV - a JAK2 mutation that results in the gene always being active. The gene produces a JAK2 tyrosine kinase that differentiates myeloid cells into erythrocytes (red blood cells). Normally, the gene is activated by erythropoietin (EPO) released by the kidneys (less so the liver) when there is tissue hypoxia. With the always active gene, erythropoietin isn't needed and the levels are low. This is important because polycythemia can also occur due to high erythropoeitin levels (chronic hypoxia, erythropoeitin secreting tumor) and checking the erythropoietin level helps differentiate secondary polycythemia from polycythemia vera.
Complications include thrombosis as well as myelofibrosis and acute leukemia.
Treatment is with serial phlebotomy which leads to iron deficiency resulting in less RBC production (lower hematocrit). Hydroxyurea is given if there is high risk of thrombosis (previous thrombosis, older age). Hydroxyurea works by suppressing the bone marrow (i.e. less cell production, less viscous blood).
Relevant Images
JAK2 tyrosine kinase receptor
Comments
Post a Comment